What is the Link between Erectile Dysfunction and Cardiovascular disease?
Men over age 65 experience some degree of erectile dysfunction (ED)1—and almost 70% of men with ED end up having coronary artery disease. 2In fact, ED can be an early warning sign of cardiovascular disease—with plaque buildup and blockage in the smaller arteries of the penis being affected sooner than the larger ones in the heart.3
Is ED can be a sign of heart Disease?

ED can be an early warning sign of heart problems
With coronary artery disease, a buildup of plaque inside the arteries can limit the amount of blood that’s able to flow through them. If the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle is reduced or blocked by this hardening of the arteries, the result can be angina (chest pain) or a heart attack.4Because the arteries that supply blood to the penis are much smaller than the ones that feed the heart, the problem may show up earlier as having difficulty getting an erection.5
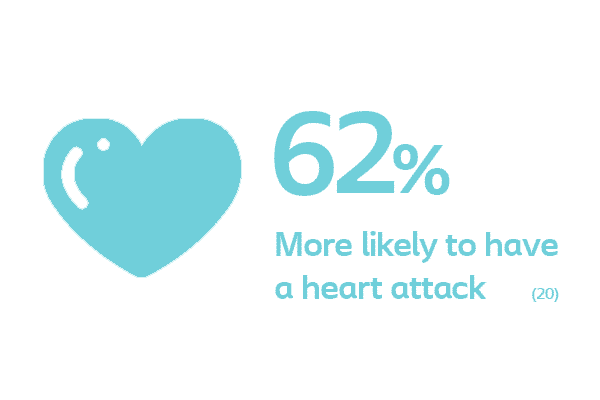
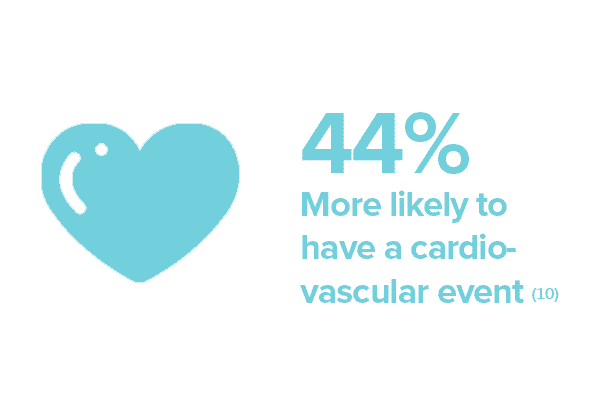
In one study that followed men for an average of six years, those with ED were:
ED is common among patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Sexual problems usually precede the onset of CVD, and should, therefore, be considered as a risk factor for cardiac events. Similarly, patients with pre-existing CVD are at increased risk of experiencing ED. Therefore, ED and CVD might be considered as two different clinical manifestations of the same systemic disease.
What it means for you
If you are experiencing ED, you should talk with your doctor about your potential risk for cardiovascular disease. And if you’re already taking certain medications such as nitrites for your heart or alpha-blockers to manage blood pressure, your doctor will discuss whether ED medications are right for you or whether other options may be more appropriate.
Take back control. Use our Specialist Finder tool to locate a doctor in your area who can provide information on how to best treat your ED.
1: Impotence. NIH: National Institutes of Health. https:consensus.nih.gov/1992/1992Impotence091html.htm.
2: Gandaglia G, Briganti A, Jackson G et al. A systematic review of the association between erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Eur Urol. 2014 (65):968-978. 2.
3: Gandaglia G, Montorsi F, Montorsi P. Management of erectile dysfunction in patients with preexisting cardiovascular disease. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2016 May;17(5):356-62.
4: NIH National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, What is Coronary Heart Disease? (n.d.) Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/cad
5: Thompson IM, Tangen CM, Goodman PJ et al. Erectile dysfunction and subsequent cardiovascular disease. JAMA 2005; 294(23):